Developmental delay refers to a significant lag in the acquisition of skills and abilities typically expected for a child’s age group. It can affect various areas of development, including cognitive, motor, speech and language, and social-emotional skills.
Causes of Developmental Delay
Developmental delay can have numerous underlying causes. Some of the common factors include:
Genetic Factors
Genetic conditions like Down, Fragile X, and Rett syndrome can lead to developmental delay. Gene abnormalities cause these conditions and can affect a child’s development.
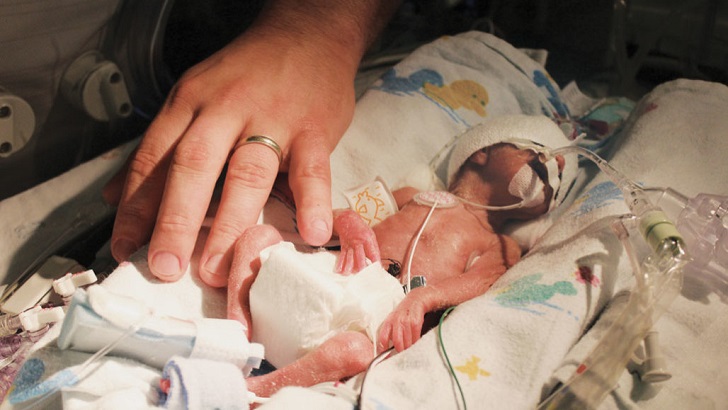
Premature Birth
Babies born prematurely are at an increased risk of developmental delay. The earlier the birth, the higher the chances of developmental challenges, as preterm infants may have underdeveloped organs and require intensive medical care.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins, malnutrition, maternal substance abuse during pregnancy, or lack of stimulation, can impact a child’s development. Adverse childhood experiences and unstable living conditions can also contribute to developmental delays.
Birth Injuries
Difficulties during childbirth, such as oxygen deprivation or trauma, can result in developmental delays. Brain injuries during birth can affect motor skills, speech and language development, and cognitive abilities.
Symptoms of Developmental Delay
The symptoms of developmental delay can vary depending on the specific area of development affected. Some common indicators include:
Delayed Motor Skills
Children may delay achieving physical milestones such as sitting, crawling, walking, or coordinating movements.
Speech and Language Delays
A child may have difficulty speaking, forming words, understanding language, or using appropriate gestures for communication.
Cognitive Challenges
Children with developmental delays may struggle with learning, problem-solving, memory, attention, or understanding abstract concepts.
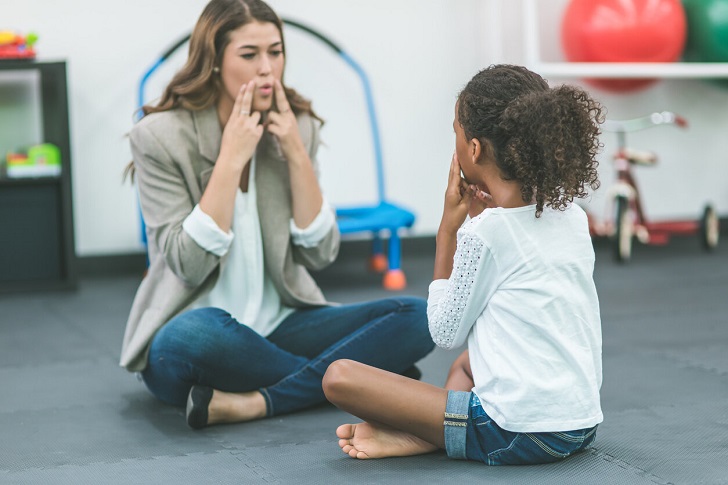

Social-Emotional Issues
Developmental delay can impact a child’s social interactions, behavior, and emotional regulation. They may struggle with making friends, showing empathy, or managing emotions.
Therapies for Developmental Delay
Early intervention is crucial for children with developmental delays, as it can significantly improve their outcomes. Various therapies and interventions are available to address different areas of developmental delay:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on improving motor skills, coordination, strength, and balance. Therapists use exercises, play-based activities, and assistive devices to help children achieve physical milestones.
Speech and Language Therapy
Speech and language therapists work with children to improve communication skills, including speech articulation, comprehension, and expressive language. They may also address difficulties with swallowing or feeding.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy aims to enhance a child’s ability to perform daily activities independently. It focuses on improving fine motor skills, sensory integration, self-care skills, and enhancing cognitive abilities related to daily functioning.

Behavioral and Psychological Interventions
Psychologists and behavior therapists may employ various techniques to address social-emotional challenges and behavioral issues associated with developmental delay. These interventions focus on improving social skills, emotional regulation, and adaptive behavior.
Educational Interventions
Children with developmental delays may require specialized educational programs tailored to their needs. Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or Individualized Family Service Plans (IFSPs) can be developed to provide targeted academic support.
Family Support and Counseling
The developmental delay affects not only the child but also their families. Family support programs and counseling can help parents cope with the challenges, guide their child’s development, and offer strategies for promoting positive outcomes.